THERMAL IMAGING - energy saving infrared - blower door test - saving report
energy Inspection
Prevents further water | Mold | Fire damage to your property and belongings.
Thermal scans are a non-disruptive method of scanning a surface to find potential problems like heat escaping through cracks, frigid incoming air or moisture that may be leaking inside.
Since our profession is generally understood to be a non-destructive, hands-off business, there is great reliance of visual inspection, eyesonly, with minimal physical interaction. Thermal imaging is well suited to this mission. It is merely a means of extending our vision beyond what we can see with the naked eye.
Energy savings audit
Thermal imagery provides an immediate look at your home condition, without having to tear anything apart to see inside the walls. A thermal imaging inspection can reveal:
- Air Sealing Cutting drafts saves 5–30%. Check outlets, windows, doors, pipes, baseboards, attic hatches.
- Leak Detection Look for rattling frames, daylight gaps. Use pressurization test with fans, incense, or damp hand.
- Sealing & Safety Apply caulk/weatherstripping. Prevent appliance backdrafts—ensure proper venting (1 sq. in./1,000 BTUs).
- Insulation Seal gaps. Insulate attic hatches, walls, basements, ducts to recommended R-values. Maintain vapor barriers and ventilation.
- HVAC & Lighting Inspect annually, change filters often, seal ducts, insulate pipes. Switch to efficient CFL/LED bulbs.
thermal imaging Can Reveal:
Thermal imagery provides an immediate look at your home condition, without having to tear anything apart to see inside the walls. A thermal imaging inspection can reveal:
- Water penetration into roofs and ceiling surfaces.
- Moisture build-up in building materials.
- Detection of missing or insufficient insulation.
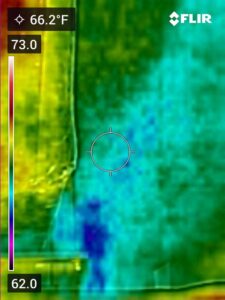

blower door test
Thermal imagery provides an immediate look at your home condition, without having to tear anything apart to see inside the walls. A thermal imaging inspection can reveal:
- Documenting the construction airtightness of buildings;
- Estimating natural infiltration rates in houses;
- Measuring and documenting the effectiveness of air-sealing activities; and
- Measuring duct leakage in forced-air distribution systems.




